
什么是 TCP/IP?
TCP/IP 是供已连接因特网的计算机进行通信的通信协议。
TCP/IP 指传输控制协议/网际协议 (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol)。
TCP/IP 定义了电子设备(比如计算机)如何连入因特网,以及数据如何在它们之间传输的标准。
接下来进行TCP,客户端以及服务器端的案例演示:
客户端
1、连接服务器Socket
2、发送消息
//客户端
public class TcpClientDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Socket socket=null;
OutputStream os=null;
try {
//1、要知道服务器的地址,编口号
InetAddress serverIP=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9999;
//2、创建一个socket连接
socket=new Socket(serverIP,port);
//3、发送消息 IO流
os=socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,欢迎来到Java语言!".getBytes());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(os!=null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
服务器
1、建立服务的端口 ServerSocket
2、等待用户的连接 accept
3、接受用户的消息
//服务端
public class TcpServerDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
Socket socket=null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos=null;
try {
//1、我得有一个地址
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(9999);
while (true){
//2、等待客户端连接过来
socket=serverSocket.accept();
//3、读取客户端的消息
is =socket.getInputStream();
baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
}
/*
*
* byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
String msg=new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
* */
//管道流
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭资源
if(baos!=null){
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is!=null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (socket!=null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(serverSocket!=null){
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
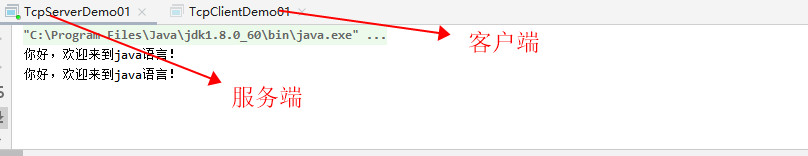
注意:先执行服务端,再去执行客户端
一. RabbitMQ 简介 MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用...
如果你想对使用手机,平板电脑和辅助技术的用户隐藏某些内容,而只对键盘用户显...
ajax传送json格式数据,关键是指定contentType,data要是json格式 如果是restful...
Afrikaans:af Albanian:sq Basque:eu Belarusian:be Bulgarian:bg Catalan:ca Ch...
今天给大家分享四个在实际开发中,比较实用的SQL Server脚本函数,希望对大家能...
本文分享自华为云社区《 架构可视化支撑系统演进探索 》原文作者无名小溪。 随着...
Linux 发行版的爱好者们又有全新的 Linux 可以体验了,日前一款名为 TeLOS 的 Li...
Eval 计算一个表达式的值并返回结果。 语法:[result = ]eval_r(expression_r) e...
一、导读 本文主要介绍Redhat7.6系统安装oracle 12201版本RAC的一些坑以及避坑方...
最近在和团队规划OKR目标的时候,我们讨论了很多问题,我先抛砖引玉,列举了一些...